
Outstanding Manufacturer of textile printing chemicals
as well as overall printing solutions provider
Keywords:
Synthetic thickener, acrylic thickener
Pigment thickener, dye printing thickener, reactive printing thickener, disperse printing thickener
Pigment binder, pigment emulsion, pigment paste
Complete classification of textile printing
1.Classification according to printing process
A. Over printing, Wet printing
Direct printing is a kind of printing directly on white fabric or on pure dyed fabric. The latter is called cover printing (also known as dye back printing). Of course, the color of the printed pattern is much darker than the background color. About 80% of the printed fabrics on the market are printed directly. (here direct printing generally refers to printing with dyes, which is different from pigment printing below)
Question: how to distinguish between white printing and dye printing?
If the background color of the fabric is the same on both sides (due to matching dyeing), and the printing pattern is much deeper than the background color, then this is the over printed fabric, otherwise it is printed on a white background.
B. Discharge Printing
The base color is dyed with dyes which are not resistant to discharge agent. After drying, the printing paste containing discharge agent or containing discharge agent at the same time is used for printing. During the post-treatment, the ground color dyes at the printing site are destroyed and the color is eliminated, forming white patterns on the color ground (called white discharge printing) or color patterns formed by dyeing of the color materials (called color discharge printing). Also known as white or color pull.
Compared with direct printing, the production cost of pullout fabric is very high, and the reductant used must be controlled carefully and accurately.

Question: how to distinguish whether the fabric is discharge printing
If the color of the positive and negative background color of the fabric is the same (because it is match dyeing), and the pattern is white or different from the background color, and the background color is relatively deep, it can be identified as discharge printing fabric. A careful examination of the reverse side of the pattern will reveal traces of the original background color (the reason for this is that the chemicals that destroy the dye cannot completely penetrate the back of the fabric).
C.Burnout printing
Burntout printing refers to printing chemical substances that can destroy the fiber structure on the pattern. As a result, the contact between chemicals and the fabric will produce holes. The edges of holes in burnt out calico are always worn early, so the fabric has poor durability. Another type of burnt out printing is that the fabric is made of blended yarn, core spun yarn, or interwoven fabric of two or more fibers. Chemicals can destroy one fiber (cellulose) and leave other undamaged fibers. This printing method can produce many special and interesting printed fabrics.

D. Foam printing
In this paper, the chemicals which can cause the fiber to expand or contract are applied to the fabric by printing method. Through proper treatment, the difference of expansion or contraction between the printed part and the non printing part fiber can be produced, so as to obtain the product with regular concave convex pattern on the surface. For example, pure cotton printed seersucker with caustic soda as expanding agent. Also called bump printing.
Foaming temperature is generally 110C, time 30 seconds, 80-100 mesh screen is selected for printing

E.Pigment Printing
Because the coating is water-insoluble coloring material and has no affinity to fiber, its coloring must be realized by coating with film-forming polymer (adhesive) and adhesion to the fiber. Pigment printing can be used in the processing of any fiber textiles, and has more advantages in printing blended fabrics and interwoven fabrics. It has the advantages of simple process, wide spectrum, clear flower outline, poor handle and low rubbing fastness. Pigment printing is direct printing with pigment, which is usually called dry printing, which is different from wet printing (or dye printing).
Their light fastness and dry cleaning fastness are good, even excellent, so they are widely used in decorative fabrics, curtain fabrics and clothing fabrics requiring dry cleaning.

Question: how to distinguish whether the fabric is pigment printing?
Pigment printing area is a little harder than the unprinted area, maybe a little thicker, especially for pigment printing with darker color, the difference is obvious.
2. Classification according to printing machinery.
A. Hand screen printing
Hand screen printing is commercially produced on long platens (up to 60 yards). The printed cloth roll is laid on the table smoothly, and the surface of the table is pre coated with a small amount of sticky material. The printer then moves the screen frame continuously by hand along the entire table, printing one frame at a time, until the fabric is completely printed. Each mesh frame corresponds to a printing pattern. The production speed of this method is 50-90 yards per hour, and commercial manual screen printing is also widely used to print cut pieces. Hand screen printing is also used to print limited, highly fashionable women's clothing and small batches of products for market exploration.to printing machinery
B. Flatbed Printing
The printing mould is a polyester or nylon screen (pattern plate) which is fixed on the square frame and has hollow pattern. The pattern on the pattern can pass through the color paste, and the area without pattern is sealed with polymer film. During printing, the pattern plate presses the fabric tightly, and the paste is filled on the pattern plate, and then scraped repeatedly with a scraper to make the paste reach the surface of the fabric through the pattern. Flat screen printing process is intermittent rather than continuous, so the production speed is not as fast as round screen.
The production rate is about 500 yards per hour.
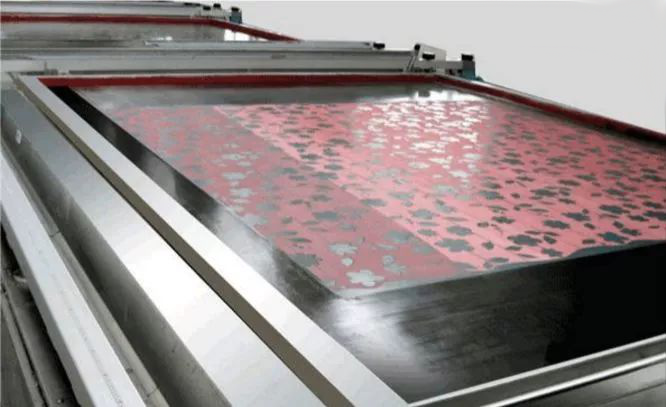

C. Rotary Screen Printing
The printing mould is a cylindrical nickel screen with hollow pattern, which is installed above the rubber guide belt in a certain order and can rotate synchronously with the guide belt. During printing, the color paste is input into the screen and stored at the bottom of the screen. When the round screen rotates with the guide belt, the scraper pressing on the bottom of the screen and the flower net have relative scraping pressure, and the color paste reaches the fabric surface through the pattern on the screen.
Rotary screen printing belongs to continuous processing with high production efficiency. The rotary screen printing process is a continuous process. The printed fabric is transported to the moving cylinder through wide rubber belt. Screen printing, rotary screen printing production speed is the fastest, more than 3500 yards per hour.
Round screen making process: black and white draft inspection and preparation - rotary screen selection - rotary screen cleaning - upper light sensitive glue - exposure - Development - baking - rubber stopper - check for use

Supplementary knowledge:
There are three methods to realize screen printing, and the application principle of each method is basically the same
The first is hand screen printing, which was very popular in 1920s and is still widely used. Until the mid-1950s, before modern technology gave this process automation, manual screen printing was the only screen printing method.
The second method is called automatic screen printing (also known as flat screen printing and automatic flat screen printing). In the mid-1960s, there was further development. The shape of screen changed from manual and automatic flat screen to round screen.
The third method is called circular screen printing or rotary screen printing. At present, the most widely used screen printing methods are rotary screen printing and flat screen printing
D. Roller printing.
Roller printing, like newspaper printing, is a high-speed process that can produce more than 6000 yards of printed fabric per hour. This method is also called mechanical printing. The copper cylinder can be engraved with very fine fine lines arranged closely, so it can print very fine and soft patterns.
If the batch production of each pattern is not very large, this method is not economical. Roller printing is the least used mass printing production method. As the fashion is becoming faster and faster, and the large-scale orders are less and less, the output of roller printing continues to decline every year.
Roller printing is often used for printing with very fine line patterns, such as Paizley vortex tweed printing and major printing patterns printed in large quantities in many seasons.
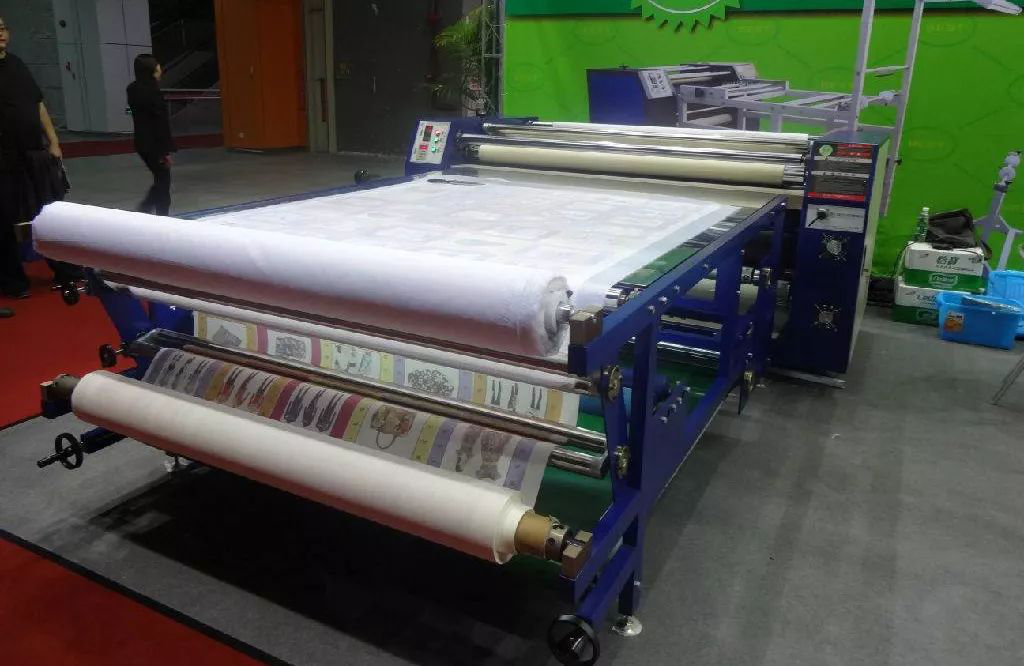

E.Tropical Printing
First, printing patterns are printed on paper with disperse dyes and printing inks, and then the printing paper (also known as transfer paper) is stored. During fabric printing, the transfer paper and un-printed face to face are pasted together through the machine through a heat transfer printing machine. Under such high temperature, the dyes on the transfer paper sublimate and transfer to the fabric to complete printing No further treatment is needed. The process is relatively simple.
Disperse dyes are the only dyes that can sublimate. In a sense, disperse dyes are the only dyes that can be used for heat transfer printing. Therefore, this process can only be applied to fabrics composed of fibers with affinity for such dyes, including acetate fiber, acrylonitrile fiber, polyamide fiber (nylon) and polyester fiber.
Heat transfer printing can be used to print cut pieces, in which case a specially designed pattern is used. As a complete fabric printing method, heat transfer printing stands out from the printing process, thus eliminating the use of large and expensive dryers, steamers, washing machines and stenters.
The production speed of continuous heat transfer printing is about 250 yards per hour. However, in the process of heat transfer, temperature and other process parameters have a great impact on the final color, so if the color light requirements are very strict, this method can not be used.

F.Digital Printing
Digital printing is to spray small dye droplets and stay at the exact position of the fabric. The nozzle and pattern formation used to spray dye liquor can be controlled by computer, and complex patterns and accurate pattern circulation can be obtained.
Digital printing printing eliminates the time delay and cost increase caused by engraving rollers and screen making, which is a competitive advantage in the fast changing textile market. The jet printing system is flexible and fast, and can quickly transfer from one pattern to another.

G. Flocking Printing
Flocking printing is a printing method in which the fiber pile (about 1 / 10-1 / 4 inch) is adhered to the fabric surface according to a specific pattern. The process is divided into two stages. First, the pattern is printed on the fabric with an adhesive rather than a dye or coating, and then the fiber lint is bonded to the fabric, which will only be fixed to the area where the adhesive has been applied. There are two ways to adhere short fiber to the surface of fabric: mechanical flocking and electrostatic flocking.
The fibers used in electrostatic flocking include all the fibers used in practical production, among which viscose fiber and durable fiber are the most common. In most cases, staple fibers are dyed before being transplanted to the fabric.
The ability of flocked fabrics to resist dry cleaning and / or water washing depends on the nature of the adhesive.
The appearance of flocked fabric can be suede, velvet, or even plush.

H. Beam Printing
Warp printing refers to printing the warp yarn of the fabric before weaving, and then weaving the fabric with plain weft (usually white), but sometimes the color of the weft is quite different from that of the printed warp. As a result, soft shadow and even fuzzy pattern effect can be obtained on the fabric.
I. Cold transfer printing
Cold transfer printing technology, also known as wet transfer printing, was introduced from Europe in the 1990s and has become a new printing method in China. It is a kind of paper printing, which is different from traditional round / flat screen printing and heat transfer printing.
The cold transfer printing machine has low tension and is suitable for printing fabrics that are easy to deform under tension, such as cotton knitted fabrics, with high production efficiency. It can also obtain better transfer printing effect for ultra-thin silk, nylon and other fabrics. It is especially good at printing complex figures and landscape patterns, with a strong sense of hierarchy and three-dimensional. The effect is comparable to that of digital direct jet printing, and the printing process achieves energy saving and emission reduction It is favored by people.
The principle of cold transfer printing is to make color paste with dyes with good solubility and stability (reactive dyes, acid dyes, etc.), adjust the surface tension between the color paste and the paper, print the image clearly on the paper coated with release agent, dry and roll. Then the fabric to be printed (softener, smoothing agent and other water repellent auxiliaries cannot be added after pretreatment) is dipped into the pretreatment solution, and then aligned with the transfer printing paper. After laminating, the pretreatment solution on the fabric dissolves the color paste on the transfer printing paper through the transfer unit. Under a certain pressure, because the affinity of dyes to fabric is greater than that of transfer paper, dyes transfer and enter the fabric pores. Finally, the paper and cloth are separated, and the fabric is dried in an oven and sent to the steamer for steaming and coloring within the specified time.
Other printing methods rarely used in textile production are: wood template printing, wax printing (i.e. wax proof) printing, yarn tie dye cloth
3. Other printing methods:
A. Double sided printing
It is similar to double-sided fabric printing on both sides, which can achieve the effect of printing on both sides of fabric. The end use is limited to double-sided sheets, tablecloths, unlined or double-sided jackets and shirts.

B. Through printing
For light-weight fabrics, such as cotton, silk and blended knitted fabrics, double-sided printing effect is sometimes required. For some of them, it needs to be turned out at the cuff or collar. The printing paste must have good vertical permeability and horizontal impermeability, so it is necessary to have special high-performance discharge printing paste.
C. Pearlescent and luminous printing
There are natural pearls and artificial pearls. Artificial pearls can be extracted from fish scales. Pearlite does not need light source excitation, acid and alkali resistance, high temperature resistance. Pearlescent printing shows the soft luster of pearl, elegant and elegant, with excellent handle and fastness. Pearlescent paste is suitable for printing of various fibers. It can be used alone or mixed with pigment to produce color pearlescent. In the process of printing, it is better to use 60-80 mesh screen. Luminous printing mainly uses the luminous crystal paste to print on the surface of the fabric, and the luminous paste is fixed on the fabric by pre drying and melting. It is mainly used in polyamide and spandex elastic interwoven products.
D. Luminous printing
Luminous powder is a kind of rare earth metal fabric. It is made into powder with a fineness of about 1 μ M. by pigment printing, luminous powder is printed on the fabric to form patterns. After a certain amount of light, the afterglow time of the flower can reach 8-12 hours, which has good luminous effect, good handle and fastness. However, it is limited to printing in light medium color.

E. Capsule printing
The micro capsule is composed of inner core and capsule coat. The inner core is dye and the capsule coating is gelatin. There are three types of microcapsules: single core type, multi-core type and composite type. The single core type contains one kind of dye, the multi-core type contains a variety of dyes, and the composite type is a composite microcapsule composed of multilayer outer films. The particle size of microcapsule dye is between 10 and 30 μ M
F. Dull printing (imitation jacquard printing)
In this paper, the pigment printing process is used to obtain the partial dull printing effect on the lustrous fabric containing the matting agent. The light and shade are clear and have the similar jacquard style. Matting slurry is usually composed of titanium dioxide or paint white as matting agent and non yellowing adhesive. It is mainly used in satin or twill silk, rayon, synthetic fiber, cellulose fiber knitted fabric and blended fabric, as well as calendered fabric and sample paper.
G. Foil Printing
Gold or silver powder is mixed with a special paste or adhesive with better transparency for gold and silver powder, and printed on the fabric to form a golden or silver flash pattern effect.

H. Sheepskin printing
The scintillator is a vacuum aluminized metal sheet with various colors, thickness of 0.008mm-0.1mm, high temperature resistance. The flicker printing should use strong adhesion, transparent film-forming and good luster, which does not affect the flashing luster and special printing paste. It is necessary to ensure that the fabric has soft handle, good fastness and brilliant effect.
I. Peach skin printing
Imitation peach skin printing is to use imported peach peel paste (or add pigment) to achieve the surface feel and appearance of peach skin after printing. Peach peel paste has strong covering power, it is more suitable for large block surface printing, and can be printed on flat screen and round screen;
J. Imitation leather printing
Imitation leather printing uses imitation leather paste and pigment to print on the fabric. After drying and baking, it can achieve leather like feel and appearance. Imitation leather pulp has good elasticity and covering power.
K. Color coating printing (glossy printing)
By using glossy paste and pigment paste, the fabric is dried and baked to obtain the effect of plastic coating and glossing
L. Photosensitive color change printing
It uses the principle of absorbing ultraviolet light and converting it into energy. The photosensitive and color changing materials are applied to printing. After printing, the products are irradiated by sunlight and ultraviolet rays, which absorb the energy of sunlight and ultraviolet rays and produce color changes. When the sun and ultraviolet rays are lost, they immediately return to the original color. The photosensitive color changing paste is the use of microcapsule technology, the fabric colorless variable color, blue variable blue purple and so on.
13. Thermochromic printing
It is printed on the fabric with temperature sensitive and color changing materials. Through the temperature change of human body, the color can be changed repeatedly. The temperature sensitive color changing paste has 15 basic colors, low temperature color, high temperature colorless, and each color is mixed and colored.